
- #Body fluid compartments calculations series
- #Body fluid compartments calculations download
- #Body fluid compartments calculations free

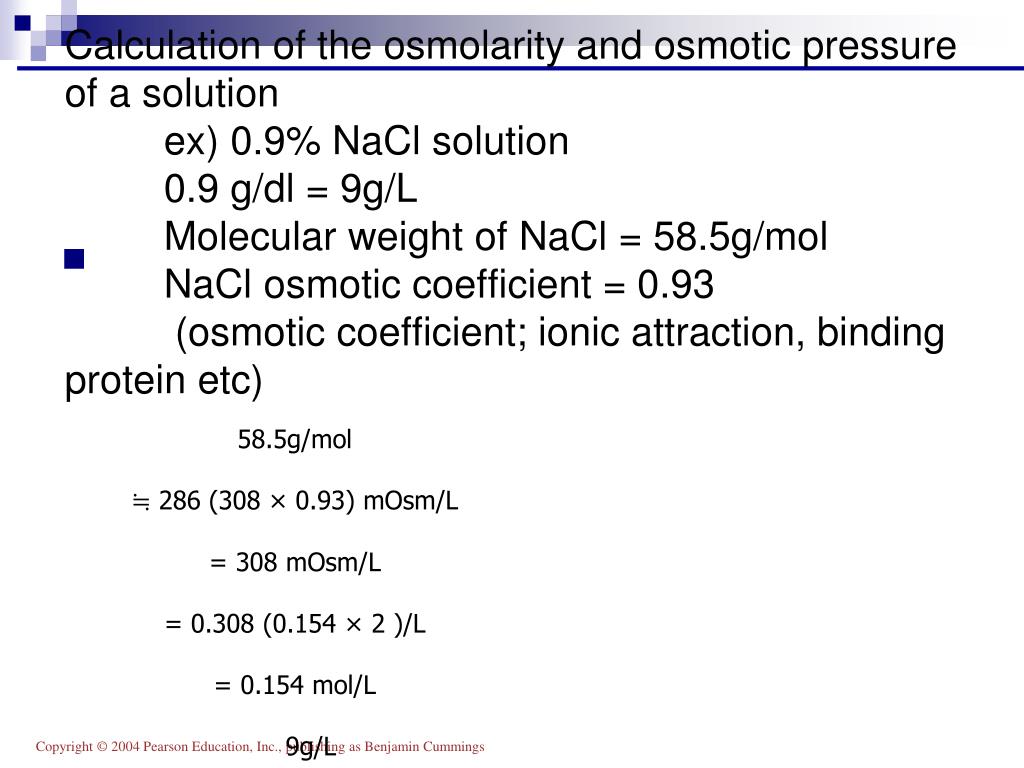
What is the volume of extracellular fluid in a healthy 75 Kg male? Where/how is this fluid distributed?.The answers can all be found in the following text. These are for you to test your current knowledge and understanding of body fluid physiology prior to reading this tutorial. Therefore it is important to have a good understanding of the physiology of normal fluid homeostasis and what happens when these mechanisms fail or are overcome. In a wide variety of illnesses and during surgery, disturbances to this fine balance occur which must be identified and corrected to prevent deterioration, complications and to promote recovery.Ĭare of unwell patients with body water abnormalities and patients undergoing surgery, are encountered daily by medical practitioners. Tight regulation of the balance between water intake and output, and its distribution, is vital to the optimal function of every organ system within the body. Report of the Task Group on Reference Manis, admittedly, a bit much for most readers.When thinking about fluid within the body we are essentially thinking about water.
#Body fluid compartments calculations download
And then they went and did it anyway. It is available for download in its entire 500 page glory, in case you ever need to refer to it for something as granular as the fluid content of a newbortn's thymus, or the normal boron concentration of human hair (0.2-0.8 mg/100 g, by the way). Of man which are known to be important or which are likely to be significant for estimation of dose from sources of radiation within or outside the body", because "however important or desirable it may be to have a Reference Man embodying all known characteristics of man, the task of defining such a Reference Man is clearly beyond the scope of the present effort". This thing was originally intended as an instrument to help scientists calculate dose following radiation exposure, and initially "it was agreed that the Task Group would limit its attention to those characteristics It is rarely referenced (because why would you), but if you dig around you will find that most of these textbooks get their information from the extensive and fascinating Report of the Task Group on Reference Man, by Snyder et al (1974).
#Body fluid compartments calculations series
This material should seem very familiar it appears in the first chapters of almost every physiology textbook, often as a series of stacked bar graphs describing the body composition of the Ideal 70kg Person.
#Body fluid compartments calculations free
Intracellular Fluid = 33% ( 23.1 litres) this volume is regulated by the movement of free water.Įxtracellular Fluid = 27% (18.9 litres) this volume is regulated by the movement of sodium. Higher in obesity, but as a lower proportion of body mass, as adipose tissue is only 10-20% water.Total body water: 42 L (60% of total body mass)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
